Foot Fungus
What is Foot Fungus?
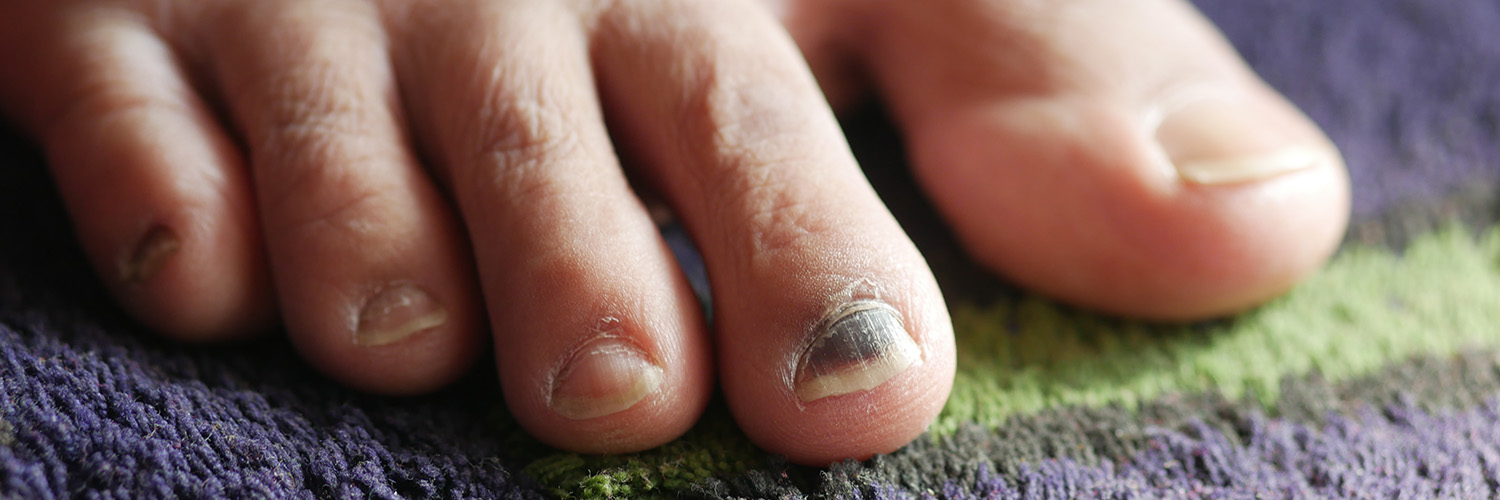
Foot fungus, commonly known as athlete’s foot (tinea pedis), is a contagious fungal infection that affects the skin on the feet. It typically begins between the toes and can spread to the soles, toenails, and even the hands if left untreated. The condition is caused by dermatophytes—fungi that thrive in warm, moist environments like sweaty socks, locker rooms, and communal showers. Although not usually serious, foot fungus can be uncomfortable and persistent without proper treatment.
What are the common symptoms of Foot Fungus?
Symptoms of foot fungus vary but often include:
- Itching, burning, or stinging sensations between the toes or on the soles
- Red, scaly, or cracked skin
- Flaky or peeling skin, especially around the toes
- Blisters or ulcers in severe cases
- A musty or unpleasant foot odor
- Thick, discolored, or crumbling toenails if the fungus spreads to the nails (onychomycosis)
The symptoms may worsen with prolonged moisture, heat, or tight footwear.
What are the common causes of Foot Fungus?
Foot fungus is primarily caused by direct or indirect exposure to fungal organisms. Common causes include:
- Walking barefoot in public areas such as pools, gyms, or locker rooms
- Wearing damp socks or sweaty shoes for long periods
- Sharing towels, shoes, or socks with an infected person
- Having sweaty feet or poor foot hygiene
- Minor skin injuries or cracks that allow fungus to enter
People with compromised immune systems, diabetes, or circulation problems are at higher risk.
What are the common treatments of Foot Fungus?
Foot fungus can usually be treated effectively with over-the-counter or prescription medications. Common treatment options include:
- Topical antifungal creams, powders, or sprays: Such as clotrimazole, terbinafine, or miconazole
- Oral antifungal medications: For persistent or widespread infections
- Proper hygiene: Washing and drying feet thoroughly, especially between the toes
- Antifungal foot soaks or medicated foot baths
- Changing socks daily and wearing breathable footwear
- Disinfecting shoes and using antifungal powder to prevent recurrence
Early treatment is important to prevent spreading and complications like nail fungus.
When should I see a doctor about Foot Fungus?
You should see a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms do not improve after using over-the-counter treatments for two weeks
- The infection spreads to other parts of the body or affects the toenails
- You have diabetes or a weakened immune system and notice signs of foot infection
- You develop blisters, ulcers, or severe swelling
- Pain or signs of a secondary bacterial infection (such as oozing or increased redness) appear
Prompt treatment can prevent further complications and stop the infection from spreading.
If you are suffering from Foot Fungus or related issues such as toenail fungus, athlete’s foot symptoms, fungal infection feet, tinea pedis, or foot hygiene, get in touch with one of our experienced podiatrists today.
Schedule an Appointment TodayContact Us
Fill out the following form to get in touch with us:
Our Locations
Innovative Foot & Ankle
Kenilworth, NJ 07033908-276-6624
Bayonne, NJ 07002201-436-4287
Montclair, NJ 07042973-783-5101

